6.2 Aufbau des Servers
Der Server besteht ebenfalls aus einem Notebook und einer Listbox. Über das Notebook wird der Server gesteuert und in der Listbox werden die Ergebnisse und Anfragen des Clients protokolliert. Der Server wird InPlace
betrieben, das heißt, er nutzt die Fläche innerhalb eines Fensters des Clients für seine Darstellung.
Wenn eine Verbindung mit dem Server besteht, der Server aber noch nicht aktiviert worden ist, wird im Bereich des Clients ein Bild dargestellt. Nach der Aktivierung erscheinen dann die Objekte des Servers im Client.
Damit der Server ablauffähig ist, wurde dem Dialog und dem Control-Objekt jeweils eine eindeutige UUID zugewiesen.
dialog IdmTest
{
.uuid "499593d0-a159-11d1-a7e3-00a02444c34e";
}
tile TiPropMethEvent "IMD_IMAGES:isaicon.gif";
default control CONTROL
{
integer Count := 0;
on start
{
CONTROL.Count := CONTROL.Count + 1;
}
on finish
{
CONTROL.Count := CONTROL.Count - 1;
if CONTROL.Count=0 then
exit();
endif
}
}
control PropMethEvent
{
.mode mode_server;
.uuid "499593d1-a159-11d1-a7e3-00a02444c34e";
.picture TiPropMethEvent;
}
6.2.1 Bereitstellung des Servers
Anders als beim Client müssen beim Server einige Schritte durchgeführt werden, damit der Server als OLE-Server betrieben werden kann.
Zunächst wird mit Hilfe der Option ‑writeole des IDM-Simulationsprogramms die zur Registrierung des OLE-Servers notwendige reg-Datei sowie die zum Bereitstellen der Ablaufkomponenten notwendige idl-Datei erzeugt. Die Kommandozeile sieht dabei wie folgt aus:
$(THIS).reg $(THIS).idl: $(THIS).dlg
$(IDM) $(THIS).dlg -localserver "$(IDM) $(THIS).dlg \
-IDMenv MODLIB=$(THISDIR) -IDMerrfile $(THIS).log" \
-writeole $(THIS)
regedit $(THIS).reg
Mit dem Befehl regedit wird der Server gleich im System registriert.
Anschließend wird die erzeugte idl-Datei mit Hilfe des MIDL-Compilers übersetzt.
$(THIS).tlb $(THIS)_p.c $(THIS).h dlldata.c: $(THIS).idl
midl /ms_ext /app_config /c_ext /tlb $(THIS).tlb /Zp1 \
/env win32 /Os $(THIS).idl
Zum Schluss wird aus den Objektdateien eine DLL generiert.
$(OUTFILE) : $(OBJS) $(TARGET).res $(DEFFILE) echo ++++++++++ echo Linking $@ echo $(LINK) > $(TARGET).lrf echo $(ENTRY) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo -def:$(THIS).def >> $(TARGET).lrf echo -out:$(OUTFILE) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo -machine:IX86 >> $(TARGET).lrf echo -subsystem:windows5.01 >> $(TARGET).lrf echo -align:0x1000 >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS1) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS2) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS3) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS4) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS5) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(OBJS6) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(TARGET).res >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(LIBS) >> $(TARGET).lrf echo $(LIBS32) >> $(TARGET).lrf link @$(TARGET).lrf del $(TARGET).lrf
Danach kann der Server von einem Client benutzt werden.
Das zugehörige Makefile sieht wie folgt aus:
THISDIR=h:\ole\clntserv
THIS=$(THISDIR)\server
IDM=idmole.exe
CL32 = -G3s
WX =
LINKDLL = /DLL
DEFDLL = -D_DLL
ENTRY = -entry:LibMain32
DEFUNICODE = -DWIN32ANSI
LINKD32 = -debug:full $(LINKDLL) -debugtype:cv
LINKN32 = -debug:none $(LINKDLL)
DEFS32 = -DWIN32 $(DEFDLL) -D_X86_=1 $(DEFUNICODE)
TLBDEFS = -DWIN32
#BOOKLIB = inole.lib
LIBS32A = msvcrt.lib kernel32.lib user32.lib gdi32.lib comdlg32.lib advapi32.lib
LIBS32B = ole32.lib oleaut32.lib uuid.lib
LIBS32 = $(LIBS32A) $(LIBS32B) $(BOOKLIB)
LIBS = rpcrt4.lib
CONTIN =
CFLAGS = -c -Od -Z7 -Ze -W3 -nologo $(CL32) \
-D_WIN32_WINNT=0x400
LINK = $(LINKD32) /NOD
DEFS = $(DEFS32) -DSTRICT -DDEBUG
.SUFFIXES: .h .obj .exe .dll .cpp .res .rc .tlb .odl
OUTFILE = $(THIS).dll
TARGET = $(THIS)
DEFFILE = $(THIS).def
OBJS1 = $(THIS)_i.obj $(THIS)_p.obj
OBJS2 = dlldata.obj libmain.obj
OBJS3 = ""
OBJS4 = ""
OBJS5 = ""
OBJS6 = ""
OBJS = $(OBJS1) $(OBJS2)
###############################################################
.c.obj:
echo ++++++++++
echo Compiling $*.c
cl $(CFLAGS) $(DEFS) $*.c
.cpp.obj:
echo ++++++++++
echo Compiling $*.c
cl $(CFLAGS) $(DEFS) $*.cpp
.rc.res:
echo ++++++++++
echo Compiling Resources
rc -r $(DEFS) $(DOC) -fo$@ $*.rc
###############################################################
all: $(THIS).reg $(THIS).idl $(THIS).tlb $(THIS).dll
clean:
del $(THIS).tlb
del $(THIS).reg
del $(THIS).dll
del $(THIS).odl
del $(THIS)_i.c
del $(THIS)_p.c
del $(THIS).h
del dlldata.c
del *.obj
del *.exe
del *.lrf
$(THIS).reg $(THIS).idl: $(THIS).dlg
$(IDM) $(THIS).dlg -localserver "$(IDM) $(THIS).dlg \
-IDMenv MODLIB=$(THISDIR) -IDMerrfile $(THIS).log" \
-writeole $(THIS)
regedit $(THIS).reg
$(THIS).tlb $(THIS)_p.c $(THIS).h dlldata.c: $(THIS).idl
midl /ms_ext /app_config /c_ext /tlb $(THIS).tlb /Zp1 \
/env win32 /Os $(THIS).idl
$(THIS)_p.obj: $(THIS)_p.c
$(THIS)_i.obj: $(THIS)_i.c
dlldata.obj: dlldata.c
libmain.obj: libmain.cpp
##############################################################
$(OUTFILE) : $(OBJS) $(TARGET).res $(DEFFILE)
echo ++++++++++
echo Linking $@
echo $(LINK) > $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(ENTRY) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo -def:$(THIS).def >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo -out:$(OUTFILE) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo -machine:IX86 >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo -subsystem:windows5.01 >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo -align:0x1000 >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS1) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS2) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS3) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS4) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS5) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(OBJS6) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(TARGET).res >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(LIBS) >> $(TARGET).lrf
echo $(LIBS32) >> $(TARGET).lrf
link @$(TARGET).lrf
del $(TARGET).lrf
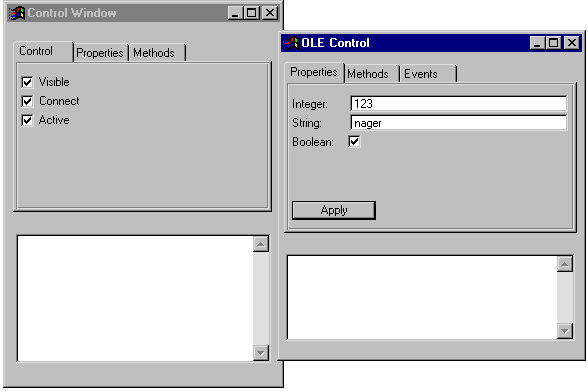
6.2.2 Abfragen und Setzen von Attributen
Damit der Client Attribute am Server abfragen kann, muss im Server nichts programmiert werden. Es können automatisch alle am Control-Objekt definierten Attribute vom Client erfragt und gesetzt werden.
Im Beispiel sind die Attribute I
, S
und B
vom Client abfragbar.
control PropMethEvent
{
integer I := 123;
string S := "Dialog Manager";
boolean B := true;
}
6.2.3 Aufruf von Methoden
Damit der Client Methoden im Server aufrufen kann, müssen diese als ganz normale Methoden des Control-Objektes definiert werden. Diese Methoden können dann auf alle im Dialog definierten Objekte und Attribute zugreifen.
In diesem Beispiel sehen die Methoden wie folgt aus:
control PropMethEvent
{
.message[1] Msg1;
.message[2] Msg2;
.message[3] Msg3;
.message[4] Msg4;
.message[5] Msg5;
.message[6] Msg6;
rule void M1
{
Info("M1() called.");
sendevent(this, Msg1);
}
rule integer M2 (integer I input)
{
Info("M2(" + I + ") called. Return -123456789");
return -123456789;
}
rule string M3 (string S input)
{
Info("M3(" + S + ") called. Return \"Bye\"");
return "Bye";
}
rule boolean M4 (boolean B input)
{
Info("M4(" + B + ") called. Return " + ( not B ));
return ( not B );
}
rule void M5 (integer I input, string S input, boolean B input)
{
Info("M5(" + I + ", " + S + ", " + B + ") called.");
}
rule string M6 (integer P1 input, string P2 input,
boolean P3 input, integer P4 input, string P5 input,
boolean P6 input, integer P7 input, string P8 input)
{
Info("M6(" + P1 + ", " + P2 + ", " + P3 + ", " + P4 +
", " + P5 + ", " + P6 + ", " + P7 + ", " + P8 +
") called. Return \"Abracadabra!\"");
return "Abracadabra!";
}
}
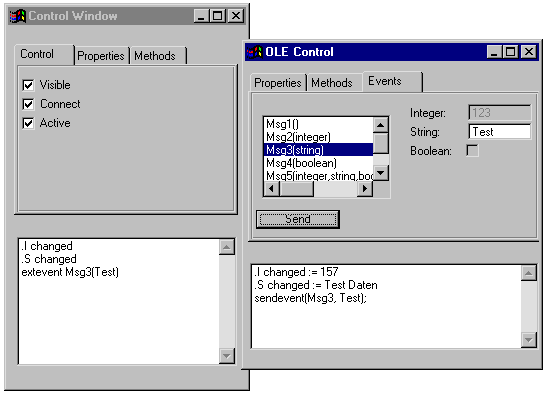
6.2.4 Versenden von Ereignissen
Wenn der Server dem Client Ereignisse schicken soll, müssen diese im Server definiert und entsprechend programmiert werden. Die Definition solcher Ereignisse erfolgt mit Hilfe der Ressource Message. Die Ereignisse werden dann mit der eingebauten Funktion sendevent an den Client geschickt.
Diese Ereignisse sind im Beispiel wie folgt definiert:
message Msg1;
message Msg2 (integer I);
message Msg3 (string S);
message Msg4 (boolean B);
message Msg5 (integer I, string S, boolean B);
message Msg6 (integer P1, string P2, boolean P3,
integer P4, string P5, boolean P6);
Zusätzlich müssen die von einem Control verschickbaren Ereignisse am Control-Objekt im Attribut .message[integer] definiert werden. Die in diesem Attribut definierten Messages werden dann an den Client weitergeleitet.
control PropMethEvent
{
.mode mode_server;
.uuid "499593d1-a159-11d1-a7e3-00a02444c34e";
.picture TiPropMethEvent;
.message[1] Msg1;
.message[2] Msg2;
.message[3] Msg3;
.message[4] Msg4;
.message[5] Msg5;
.message[6] Msg6;
}
Das Versenden der Ereignisse erfolgt nach Selektion des Pushbuttons Send
in folgender Regel:
child pushbutton PbSend
{
.yauto -1;
.height 1;
.text "Send";
.defbutton true;
integer I shadows instance NpEvents.Integer.Value;
boolean B shadows instance NpEvents.Boolean.Value;
string S shadows instance NpEvents.String.Value;
on select
{
case this.parent.LbEvents.activeitem
in 1:
sendevent(this.control, Msg1);
Info("sendevent(Msg1);");
in 2:
sendevent(this.control, Msg2, this.I);
Info("sendevent(Msg2, " + this.I + ");");
in 3:
sendevent(this.control, Msg3, this.S);
Info("sendevent(Msg3, " + this.S + ");");
in 4:
sendevent(this.control, Msg4, this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg4, " + this.B + ");");
in 5:
sendevent(this.control, Msg5, this.I, this.S, this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg5, " + this.I + ", " + this.S + ", " +
this.B + ");");
in 6:
sendevent(this.control, Msg6, this.I, this.S, this.B,
this.I, this.S, this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg6, " + this.I + ", " + this.S + ", " +
this.B + ", " + this.I + ", " + this.S + ", " +
this.B + ");");
otherwise:
Info("Error - unknown event");
endcase
}
}
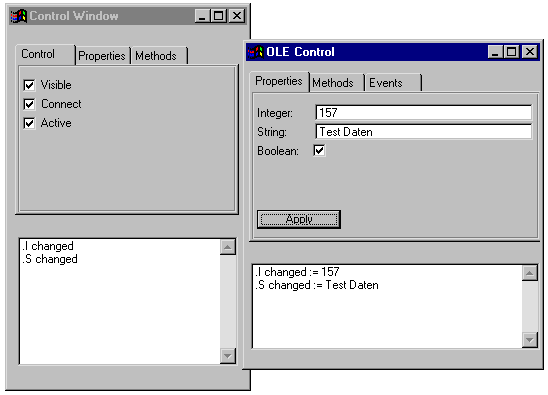
6.2.5 Versenden von Benachrichtigungen (Notifications)
Um Benachrichtigungen über die Änderungen von Attributen an den Client zu verschicken, muss im Server nichts programmiert werden. Sobald sich ein Attribut an dem Control ändert, wird automatisch eine Benachrichtigung an den Client verschickt.
Der Regelcode für die Zuweisung innerhalb des Servers sieht wie folgt aus:
child pushbutton PbApply
{
.yauto -1;
.height 1;
.text "Apply";
.defbutton true;
on select
{
this.control.I := this.parent.Integer.Value;
this.control.S := this.parent.String.Value;
this.control.B := this.parent.Boolean.Value;
}
}
6.2.6 Der Server Dialog
dialog IdmTest
{
.uuid "499593d0-a159-11d1-a7e3-00a02444c34e";
}
tile TiPropMethEvent "IMD_IMAGES:isaicon.gif";
message Msg1;
message Msg2(integer I);
message Msg3(string S);
message Msg4(boolean B);
message Msg5(integer I, string S, boolean B);
message Msg6(integer P1, string P2, boolean P3,
integer P4, string P5, boolean P6);
model groupbox MInteger
{
.height 1;
.xauto 0;
integer Value := 123;
child statictext { .text "Integer:"; }
child edittext Et
{
.xleft 8;
.xauto 0;
.format "%-9d";
.content "123";
on charinput
{
if fail(this.parent.Value := atoi(this.content)) then
this.parent.Value := 0;
endif
}
}
on .Value changed
{
this.Et.content := itoa(this.Value);
}
}
model groupbox MString
{
.height 1;
.xauto 0;
string Value shadows instance MString.Et.content;
child statictext { .text "String:"; }
child edittext Et
{
.xleft 8;
.xauto 0;
.content "Dialog Manager";
}
}
model groupbox MBoolean
{
.height 1;
boolean Value shadows instance Cb.active;
child statictext { .text "Boolean:"; }
child checkbox Cb
{
.xleft 8;
.text "";
}
}
default control CONTROL
{
integer Count := 0;
on start
{
CONTROL.Count := CONTROL.Count + 1;
}
on finish
{
CONTROL.Count := CONTROL.Count - 1;
if CONTROL.Count=0 then
exit();
endif
}
}
model control PropMethEvent
{
.mode mode_server;
.uuid "499593d1-a159-11d1-a7e3-00a02444c34e";
.picture TiPropMethEvent;
.message[1] Msg1;
.message[2] Msg2;
.message[3] Msg3;
.message[4] Msg4;
.message[5] Msg5;
.message[6] Msg6;
integer I := 123;
string S := "Dialog Manager";
boolean B := true;
rule void M1
{
Info("M1() called.");
sendevent(this, Msg1);
}
rule integer M2 (integer I input)
{
Info("M2(" + I + ") called. Return -123456789");
return -123456789;
}
rule string M3 (string S input)
{
Info("M3(" + S + ") called. Return \"Bye\"");
return "Bye";
}
rule boolean M4 (boolean B input)
{
Info("M4(" + B + ") called. Return " + ( not B ));
return ( not B );
}
rule void M5 (integer I input, string S input, boolean B input)
{
Info("M5(" + I + ", " + S + ", " + B + ") called.");
}
rule string M6 (integer P1 input, string P2 input,
boolean P3 input, integer P4 input, string P5 input,
boolean P6 input, integer P7 input, string P8 input)
{
Info("M6(" + P1 + ", " + P2 + ", " + P3 + ", " + P4 +
", " + P5 + ", " + P6 + ", " + P7 + ", " + P8 +
") called. Return \"Abracadabra!\"");
return "Abracadabra!";
}
on .I changed
{
Info(".I changed := " + this.I);
this.Gb.Nb.NpProperties.Integer.Value := this.I;
}
on .S changed
{
Info((".S changed := " + this.S));
this.Gb.Nb.NpProperties.String.Value := this.S;
}
on .B changed
{
Info((".B changed := " + this.B));
this.Gb.Nb.NpProperties.Boolean.Value := this.B;
}
child groupbox Gb
{
.xauto 0;
.yauto 0;
.borderwidth 0;
child notebook Nb
{
.xauto 0;
.yauto 1;
.height 10;
child notepage NpProperties
{
.active true;
.title "Properties";
child MInteger Integer { }
child MString String { .ytop 1; }
child MBoolean Boolean
{
.ytop 2;
.Value := true;
}
child pushbutton PbApply
{
.yauto -1;
.height 1;
.text "Apply";
.defbutton true;
on select
{
this.control.I := this.parent.Integer.Value;
this.control.S := this.parent.String.Value;
this.control.B := this.parent.Boolean.Value;
}
}
}
child notepage NpMethods
{
.active false;
.title "Methods";
child listbox LbMethods
{
.xauto 0;
.yauto 0;
.content[1] "void M1()";
.content[2] "integer M2(integer)";
.content[3] "string M3(string)";
.content[4] "boolean M4(boolean)";
.content[5] "void M5(integer, string, boolean)";
.content[6] "string M6(integer, string, boolean, ...\
integer, string, boolean, integer, string)";
.firstchar 1;
}
}
child notepage NpEvents
{
.title "Events";
child listbox LbEvents
{
.xauto 1;
.width 20;
.yauto 0;
.ybottom 1;
.content[1] "Msg1()";
.content[2] "Msg2(integer)";
.content[3] "Msg3(string)";
.content[4] "Msg4(boolean)";
.content[5] "Msg5(integer, string, boolean)";
.content[6] "Msg6(integer, string, boolean, ...\
integer, string, boolean)";
.activeitem 1;
.firstchar 1;
on select
{
this.parent.Integer.sensitive :=
(0 <> stringpos(this.content[this.activeitem],
"integer"));
this.parent.String.sensitive :=
(0 <> stringpos(this.content[this.activeitem],
"string"));
this.parent.Boolean.sensitive :=
(0 <> stringpos(this.content[this.activeitem],
"boolean"));
}
}
child MInteger Integer
{
.sensitive false;
.xleft 22;
.yauto 1;
.Et.active false;
}
child MString String
{
.sensitive false;
.xleft 22;
.yauto 1;
.ytop 1;
}
child MBoolean Boolean
{
.sensitive false;
.xleft 22;
.yauto 1;
.ytop 2;
}
child pushbutton PbSend
{
.yauto -1;
.height 1;
.text "Send";
.defbutton true;
integer I shadows instance NpEvents.Integer.Value;
boolean B shadows instance NpEvents.Boolean.Value;
string S shadows instance NpEvents.String.Value;
on select
{
case this.parent.LbEvents.activeitem
in 1:
sendevent(this.control, Msg1);
Info("sendevent(Msg1);");
in 2:
sendevent(this.control, Msg2, this.I);
Info("sendevent(Msg2, " + this.I + ");");
in 3:
sendevent(this.control, Msg3, this.S);
Info("sendevent(Msg3, " + this.S + ");");
in 4:
sendevent(this.control, Msg4, this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg4, " + this.B + ");");
in 5:
sendevent(this.control, Msg5, this.I, this.S,
this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg5, " + this.I + ", " + this.S +
", " + this.B + ");");
in 6:
sendevent(this.control, Msg6, this.I, this.S,
this.B, this.I, this.S, this.B);
Info("sendevent(Msg6, " + this.I + ", " + this.S +
", " + this.B + ", " + this.I +
", " + this.S + ", " + this.B +
");");
otherwise:
Info("Error - unknown event");
endcase
}
}
}
}
child listbox LbInfo
{
.xauto 0;
.yauto 0;
.ytop 10;
.firstchar 1;
}
}
on extevent 1
{
sendevent(this,Msg3,"Bye event");
this:sendevent(Msg4, true);
}
}
rule void Info (string S input)
{
LbInfo.content[(LbInfo.itemcount + 1)] := S;
LbInfo.topitem := LbInfo.itemcount;
}
on IdmTest extevent 1(object C)
{
Info("on IdmTest extevent 1");
sendevent(C, Msg2, 909);
}