Easily connect user interface and data sets with automatic data updating.
Key features
- Separation between user interface and application and data storage according to the Model-View-Presenter (MVP) design pattern.
- Automatic updating between interaction objects and data, where the update time can be defined by options.
- Connection of any attributes of the GUI objects with data structures, e.g. to control visibility and usability depending on data.
- Automatic conversion of data to the required data type.
- Data types for data in list and matrix form as well as language elements and functions for dealing with these data types.
Functions
Another feature of ISA Dialog Manager 6 is the data model, combined with data types for list and matrix data structures. The data model forms an additional abstraction layer between the user interface on the one hand and the application and data storage on the other.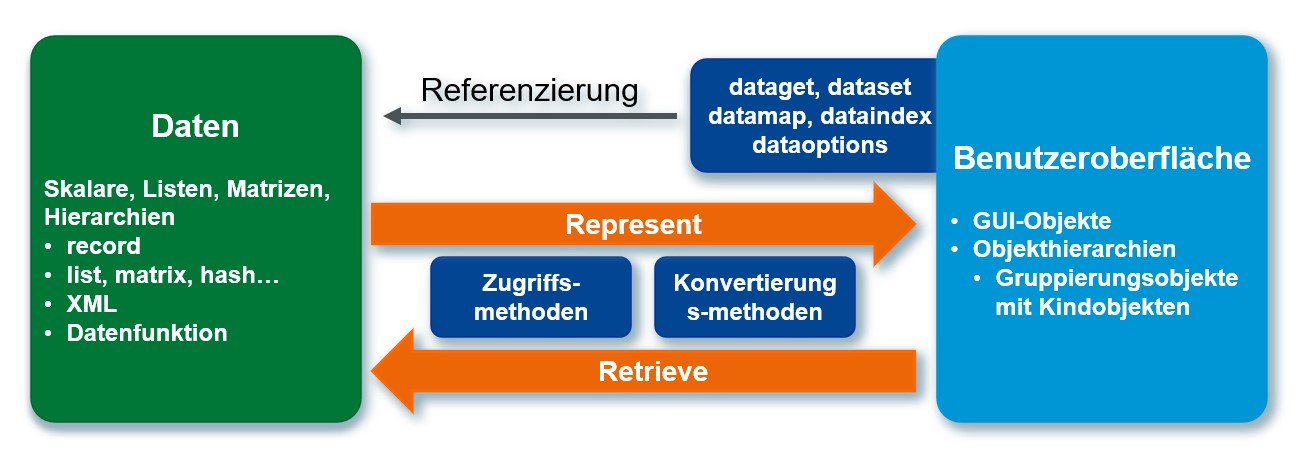
With the IDM data model, you can fill the objects of your user interfaces with data and incorporate changes into the data through user input. Connections between GUI objects and data structures are established by setting attributes. The ISA Dialog Manager then takes over the updating of the data. You do not need to write any code for this update. You can specify when the updates occur through options. The ISA Dialog Manager converts the data into the required data type. For example, an integer value can be automatically converted to Boolean to control the Visible attribute of an object.
IDM objects, e.g. B. Records and variables or XML documents are used. In addition, interaction objects can be bound to data functions. To represent the data, the data model calls the Represent method of the connected objects. You can override this method according to your needs, such as formatting the data.
New data types
The data model also introduced new data types for list and matrix structures in the ISA Dialog Manager. These include:
- list: List with values of different data types;
- vector: List of values of the same data type;
- matrix: Two-dimensional field with arbitrary values;
- hash: Associative field with key-value pairs.
With the new data types you can, for example, fill list objects and tables with a single assignment.
The rule language has been supplemented with language elements for working with these data types, for example a foreach Loop to iterate through lists or matrices. Existing built-in functions have been extended to handle the new data types. Additionally, there are new built-in functions, for example keys() and values()to access the keys and values of an associative field (hash).
You can find a commented Sample Dialog for the new Data Model here.
